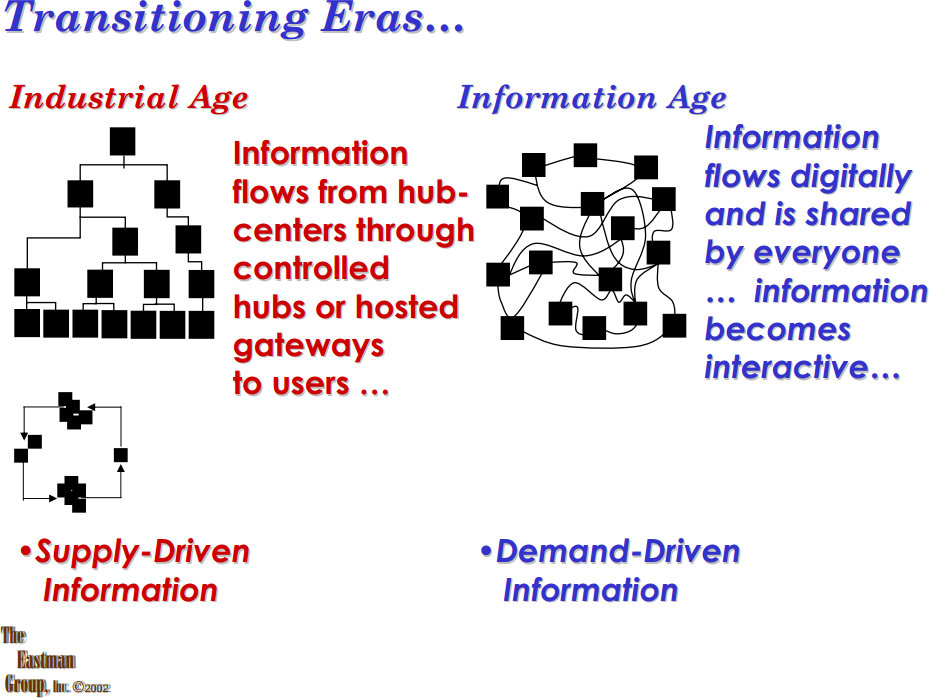
This last week began with a client in North America, continued with a call from a subject matter expert in South America and culminated in two discussions I commented a bit longer on. Triggering this new article talking about “digital in aviation”, pioneering days and the impact of dinosaurs. And why we suffer in aviation from too much #talkthetalk
Not Invented Here, part 1
 Last week, I had a lengthy phone call with an airport manager in the U.S. Snow-Belt, asking me about ideas, how to break up the silo thinking that keeps all his ideas about a common airport operations center as a basis for some A-CDM-style development from moving forward. Next winter approaching, he’s worried about repeating the past years’ experience of unnecessary delays. “The airline always knows better” he complained to me. If we offer them solution, it’s not theirs, so it’s being turned down. Communication is faulty and in crisis, everyone works on their own. #talkthetalk
Last week, I had a lengthy phone call with an airport manager in the U.S. Snow-Belt, asking me about ideas, how to break up the silo thinking that keeps all his ideas about a common airport operations center as a basis for some A-CDM-style development from moving forward. Next winter approaching, he’s worried about repeating the past years’ experience of unnecessary delays. “The airline always knows better” he complained to me. If we offer them solution, it’s not theirs, so it’s being turned down. Communication is faulty and in crisis, everyone works on their own. #talkthetalk
Passengers spend 156 Minutes at AMS
 Now give me a break. When I read this “promo” on LinkedIn, is it just me, seeing the fault in it?
Now give me a break. When I read this “promo” on LinkedIn, is it just me, seeing the fault in it?
As I outlined 2011 and 2014 in my two posts about a contemporary check-in process, contemporary airport passenger processes, to be attractive for the passenger, we need to minimize the wait time, the “ineffective” time spend at airports! It’s the big advantage of regional aviation, to minimize airport spent time.
Planning my current travels, I will spend some time with the family in Northern Germany, in between two events in Switzerland. In both cases, traveling eight hours by train will reflect in several hundred Euros in cost savings, and adds less than an hour on the total travel time door-to-door. As no, the meetings are not in Zürich.
This reminded me of the time we pioneered online travel booking (today Amadeus’ Cytric™). Own story. But as I mentioned back in 2018, compared to those pioneering days, development has almost come to a halt, with just little cosmetics and changes to the functionalities. Very little real improvements.
Working on what was to become Cytric and the first commercially used corporate online booking tool, we discussed:
The Multimodal Approach
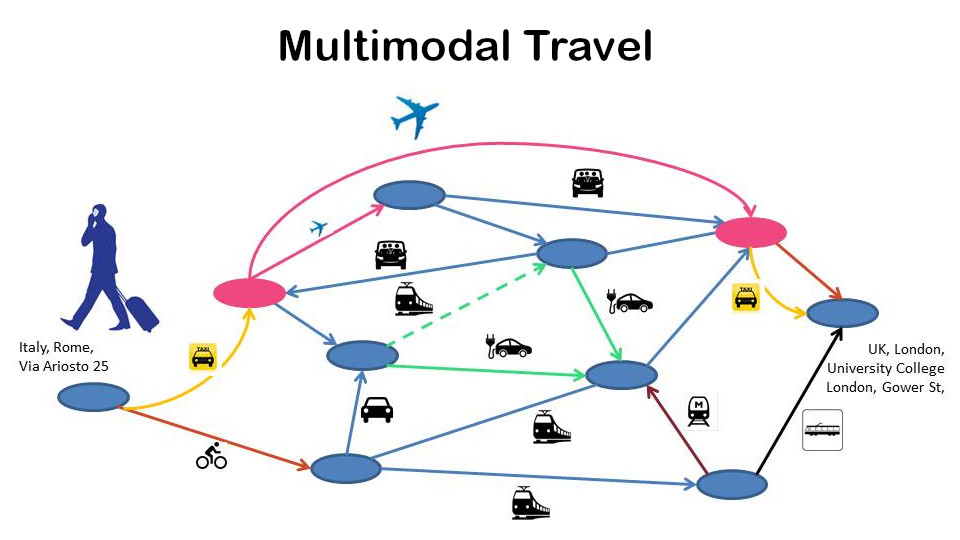 Our vision for what was to be Cytric, that we wanted to follow, a vision not existing now, 25 years later, was to enter the home address, the destination address and the system would provide you the best travel options for you to get to the airport using car, rail, taxi, whatever, fly towards your destination and again take rail, taxi, rental car, whatever, to get to where you needed to go.
Our vision for what was to be Cytric, that we wanted to follow, a vision not existing now, 25 years later, was to enter the home address, the destination address and the system would provide you the best travel options for you to get to the airport using car, rail, taxi, whatever, fly towards your destination and again take rail, taxi, rental car, whatever, to get to where you needed to go.
Back in those days, we already understood that it’s not about the flight. Or rail. The customer, especially the business traveler, needs to go somewhere. Getting to and from the airport, the check-in process and delays, connecting and waiting for the connecting flight, getting off the airport, all adds to the travel time. But even mighty Google only offers me to select one mode of transport, i.e. car, rail or flight… #talkthetalk
Travel Agent or Data Processor?
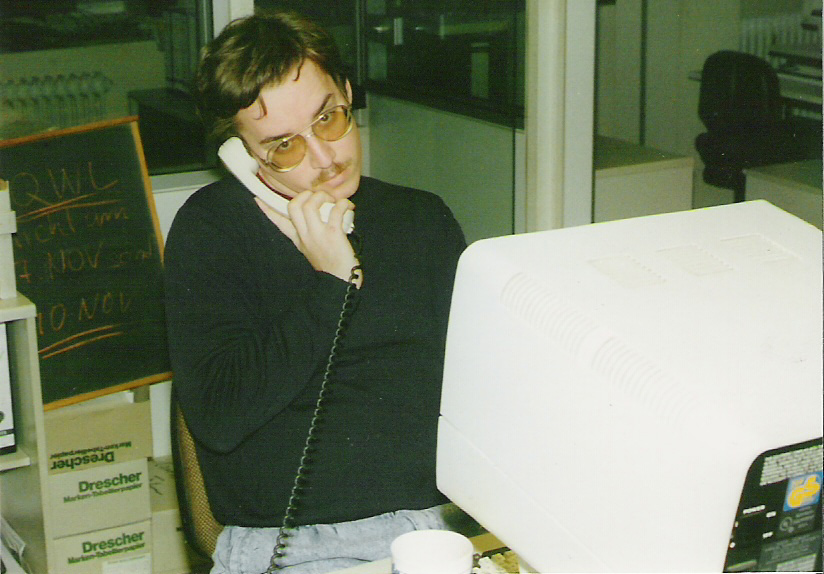 Speaking about Business Travel Management, we don’t need data typists any more. In the good old days, travel agents were the experts, knowing how to get the traveler from A to B, halfway (or all) around the world… Then came the GDS and the travel agents became data interfaces to the big data accessed through travel computers being connected with mighty servers. Something we call cloud computing today, using “dummy terminals”. Using codes like AN19DECFRAMIA and SS1B1M2 to search for and book a flight. Or similar complicated tools to book a rail ticket.
Speaking about Business Travel Management, we don’t need data typists any more. In the good old days, travel agents were the experts, knowing how to get the traveler from A to B, halfway (or all) around the world… Then came the GDS and the travel agents became data interfaces to the big data accessed through travel computers being connected with mighty servers. Something we call cloud computing today, using “dummy terminals”. Using codes like AN19DECFRAMIA and SS1B1M2 to search for and book a flight. Or similar complicated tools to book a rail ticket.
(And yes, that’s me in the American Airline office back in 1987 at an “ICOT” terminal.)
Then we enabled online booking and all that easy trips anyone can “book” now without any help. But what if you want to combine several destinations? What if you’re not living in Frankfurt or Paris, but in a rural, small industrial town with not many flights? We need the real travel agents again. Not the data processors. We need travel experts, that require strong and ongoing training and some specialization to provide the customer with a solution to their travel needs. That think beyond computer algorithms and understand “cross tickets” or “interlining” or multimodal travel. That take into account getting from and to the transportation hubs. And less conservatism, opposition to change and other #talkthetalk
Total Travel Time
 It is why I believe we need regional aviation and we need more of it. Smaller aircraft, connecting secondary cities, offering quick and direct connection. Hubs are good for the global networks. And as I kept and keep emphasizing. Regional airports must not look out, how to get their locals out to the world. But to justify their existence, they need to bring the world to their regions! If that is by car, bus, train and/or flight is irrelevant for the passenger. To offer good connections at competitive cost and speed is the task at hand. And no, there is no reason for #flygskam if you do that right.
It is why I believe we need regional aviation and we need more of it. Smaller aircraft, connecting secondary cities, offering quick and direct connection. Hubs are good for the global networks. And as I kept and keep emphasizing. Regional airports must not look out, how to get their locals out to the world. But to justify their existence, they need to bring the world to their regions! If that is by car, bus, train and/or flight is irrelevant for the passenger. To offer good connections at competitive cost and speed is the task at hand. And no, there is no reason for #flygskam if you do that right.
We need holistic thinking. Beyond our petty box. And less #talkthetalk
The “C” in A-CDM
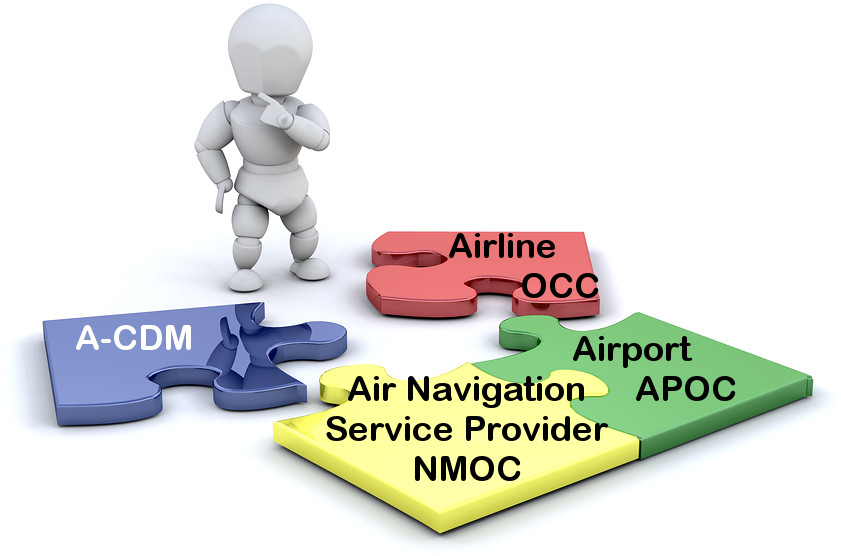 On the call from an aviation IT professional it triggered that A-CDM is for big airports only. Is it?
On the call from an aviation IT professional it triggered that A-CDM is for big airports only. Is it?
Also the first article today on LinkedIn was from my friend Kalle Keller about TAM (Total Airport Management) and A-CDM.
As I outlined in my articles on that topic and i.e. the article about the Polar Vortex + Collaboration, A-CDM is about the C: Collaboration! It’s not what EuroControl, with their own agenda of this, markets as A-CDM. Neither that “bible” of theirs, they call the Airport Collaborative Decision Making (A-CDM) Implementation Manual. A “bible” about everyone I speak to reads and believes it to be the holy grail. It isn’t.
 As I approached it back in 2016/17 and shared the learning curve at Passenger Terminal Expo 2017, the first step into A-CDM is and must always be a collaborative approach between the stakeholders at the airport. Systems and IT are secondary. Less than secondary! It is about tearing down siloes in the heads, between the stakeholders. The development of a common understanding of the common goal to optimize the processes for the greater good: A smooth management of airport operations beyond “the operations management”. Overall. Holistic.
As I approached it back in 2016/17 and shared the learning curve at Passenger Terminal Expo 2017, the first step into A-CDM is and must always be a collaborative approach between the stakeholders at the airport. Systems and IT are secondary. Less than secondary! It is about tearing down siloes in the heads, between the stakeholders. The development of a common understanding of the common goal to optimize the processes for the greater good: A smooth management of airport operations beyond “the operations management”. Overall. Holistic.
And unfortunately, only once you did your homework at the airport … or the airline … the air traffic control, only then you can reach out to integrate with other A-CDM systems. And beyond. Not behind paywalls, but sharing for joint process improvements.
But then I research airports and my birth country Germany, mighty pacemaker in A-CDM, the ANSP (German Air Traffic Control) hides the basic aviation data from the Aeronautical Information Publication (AIP) is hidden behind a paywall. So other sites, like OpenStreetMaps, Wikipedia, etc. are forced to use secondary sources. Are you kidding me? And yes, even for countries with a truly open AIP, we find some 10% of discrepancies on the data. As those AIPs are published as PDF, not as data tables to quickly update. And the IATA code search is full of airports defunct for years. As they simply “add” but never check… And hide their misery behind a paywall? #talkthetalk
OTA + NDC – Barrel Bursts
 An older article addressed NDC, the “New Distribution Capability” as a barrel burst. And reminded me of my project back in 2006/07, when we tried to develop a common database for hotel-information (descriptive) based on the OpenTravel Alliance XML standards that I had originally worked on in the early days. The standard has been so blown-up, that you simply can’t “comply” with a standard set of features, but anyone can pick what they want and that not being the same that others use, we have an overblown “standard” that in practical life allows everyone to be compliant, but still speaking totally different languages.
An older article addressed NDC, the “New Distribution Capability” as a barrel burst. And reminded me of my project back in 2006/07, when we tried to develop a common database for hotel-information (descriptive) based on the OpenTravel Alliance XML standards that I had originally worked on in the early days. The standard has been so blown-up, that you simply can’t “comply” with a standard set of features, but anyone can pick what they want and that not being the same that others use, we have an overblown “standard” that in practical life allows everyone to be compliant, but still speaking totally different languages.
The same is with NDC. Original idea of NDC was to allow standard packaging of new or unique parts into the package. I recall early discussions when airlines started to unravel their travel packages and thought a way to package their individualized offers with new and unique ancillaries. The demand was to overcome the limitations of the smallest common denominator represented by the classic GDS. Nowadays, the GDS-ability to manage NDC is a key driver… In my opinion, the original intend was completely turned around. It’s now focused on a solution to put anything the airline comes up with in boxes that the GDS can manage.
As a bold example, we had the AIRIMP back in the 80s. To date, it is the smallest common denominator all airlines work with. Even though, a large number of functionalities specified in the AIRIMP are amiss in all those hip online (flight) booking interfaces (here’s the AIRIMP’s table of content). 26 years after we did the first commercial flight bookings on the web. Again a lot of #talkthetalk, tons of bold ideas how to make things better, whereas the basics are not yet covered? #talkthetalk
Disruption Management

A-CDM and TAM are in a large part about disruption management. Ten years ago we talked about “situational awareness” to manage disruptions. And I ask the same question ever since. I would like to see a tool that reflects the contemporary visualization of not what hits us now, but to see, how our industry-partner’s efforts impact the setbacks from weather, technical etc. – to identify hours ahead bottlenecks from aircraft delays, crews exceeding their duty hours, technical problems, peaks exceeding capacity, ATC problems, ground problems.
To do this, we must exchange data in large scale. All I see is data siloes and paywalls and a distrust to share data, keeping defunct and outdated processes alive, but no vision of collaboration on an industry scale. That even no matter that the same data is available in island solutions on interfaces like flightradar or the individual airports’ websites. #talkthetalk
The Source of the Most Common Truth
 Our main problem is that our Powers-That-Be still consider themselves in a competition. Data is value, so put it in siloes. Where OpenStreetMap enabled mapping solutions, aviation data is still locked away. It takes two months until IATA publishes passenger data, after four months those numbers happen to differ substantially.
Our main problem is that our Powers-That-Be still consider themselves in a competition. Data is value, so put it in siloes. Where OpenStreetMap enabled mapping solutions, aviation data is still locked away. It takes two months until IATA publishes passenger data, after four months those numbers happen to differ substantially.
Looking at ICAO vs. the national AIP data, there are differences aplenty, worse even for IATA. So instead of working all together to manage common data together, we have different sources with different data. It is what I learned at SITA to be the art to find “The Source of the Most Common Truth”. There are industries living to develop and manage tools to overcome standard industry messages with airlines adding non-standard “features” to their messages, forcing rejects and delayed processing.
Back in 1995, Bill Gates spoke about the Internet about “Information at your Fingertips”. For the aviation, that is #talkthetalk
Status Quo + Outlook
 Where aviation in the 1960s to -80s was a pacemaker in global eCommerce, it is now limping behind. Can tell stories about replies from industry bodies when I informed them about factual mistakes in their data. And their ignorance shown by neither directing the report to their PTBs, nor updating the faulty information. Instead of working together to develop the aviation of the future, we have conservative forces in play that hinder real development. Be that about A-CDM, data interfaces, data intelligence. We limp behind and instead of doing, we #talkthetalk.
Where aviation in the 1960s to -80s was a pacemaker in global eCommerce, it is now limping behind. Can tell stories about replies from industry bodies when I informed them about factual mistakes in their data. And their ignorance shown by neither directing the report to their PTBs, nor updating the faulty information. Instead of working together to develop the aviation of the future, we have conservative forces in play that hinder real development. Be that about A-CDM, data interfaces, data intelligence. We limp behind and instead of doing, we #talkthetalk.
Sure the same is true on sustainable aviation, but that’s another topic I discussed and discuss in other blog articles.
To overcome this, we must strengthen IATA and ICAO and demand the change from our PTBs. Stop the paywalls, speed up the availability of LIVE KPIs. Once a flight is finished the data must be available. Not tomorrow. All else is #talkthetalk.
My humble opinion. Happy to discuss how we can encourage real CHANGE.
Food for Thought
Comments welcome
 P.S.: While I wrote this article, Germania, an airline that I know from the beginning of my career, who’s team I booked at
P.S.: While I wrote this article, Germania, an airline that I know from the beginning of my career, who’s team I booked at 

 Lesson learned from my research about Zürich delays: It very often is cheaper for the airline to cancel the flight to make sure the further aircraft “rotation” (planned flights for the remaining day/week) are not impacted. Especially if i.e. winter operations allow for “higher force” reasoning of the cancellation. While the airline can show goodwill and help the stranded passengers, in such situation they are not legally forced to add the legal, excessive passenger compensation for delays. It also in fact reduces the overall passenger upset. And Zürich can predict the delays!
Lesson learned from my research about Zürich delays: It very often is cheaper for the airline to cancel the flight to make sure the further aircraft “rotation” (planned flights for the remaining day/week) are not impacted. Especially if i.e. winter operations allow for “higher force” reasoning of the cancellation. While the airline can show goodwill and help the stranded passengers, in such situation they are not legally forced to add the legal, excessive passenger compensation for delays. It also in fact reduces the overall passenger upset. And Zürich can predict the delays!

 Clear as can be, there is no “software panacea” either. In North America, the closest thing in my experience is
Clear as can be, there is no “software panacea” either. In North America, the closest thing in my experience is 
![“Our Heads Are Round so our Thoughts Can Change Direction” [Francis Picabia]](https://foodforthought.barthel.eu/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/Picabia-Francis-Round-Heads.jpg)
 While doing the research at late delair for the Zurich Airport case study, focusing on the impact of a contemporary deicing management, just that improvement in (IT-supported) process saved about 20 million in one winter alone there. For Swiss (about 50% of the flights). Now working on a financial summary that thanks to the acquisition of delair by SITA never made it “to market”, I spoke with the OCC (Operations Control Center) manager of Swiss in Zurich. Who confirmed what they all knew (and know), but their management remains blissfully ignorant about: It is all about rotations in an airline. The aircraft starts somewhere in the morning and flies to different places throughout the day. And a disruption or delay anywhere en-route is prone to impact the entire rotation. Worse, a late aircraft usually accumulates more delays as ground handling is also tightly scheduled without spare manpower to cover up for such situations. Then crews fall out of schedule as they have to have their rest times. And while the airline may reduce the financial damage by calling for higher force on a snow event in the morning, on the flights down the line, I am told they tend to pay. And passenger compensation often exceeds the value of a single ticket!
While doing the research at late delair for the Zurich Airport case study, focusing on the impact of a contemporary deicing management, just that improvement in (IT-supported) process saved about 20 million in one winter alone there. For Swiss (about 50% of the flights). Now working on a financial summary that thanks to the acquisition of delair by SITA never made it “to market”, I spoke with the OCC (Operations Control Center) manager of Swiss in Zurich. Who confirmed what they all knew (and know), but their management remains blissfully ignorant about: It is all about rotations in an airline. The aircraft starts somewhere in the morning and flies to different places throughout the day. And a disruption or delay anywhere en-route is prone to impact the entire rotation. Worse, a late aircraft usually accumulates more delays as ground handling is also tightly scheduled without spare manpower to cover up for such situations. Then crews fall out of schedule as they have to have their rest times. And while the airline may reduce the financial damage by calling for higher force on a snow event in the morning, on the flights down the line, I am told they tend to pay. And passenger compensation often exceeds the value of a single ticket! In 2014 I wrote
In 2014 I wrote  And while the airlines benefit, I hear from the airports that they do not show any interest in A-CDM and A-CDM improvements. While they cut into the flesh on most airport’s fees, while they let them starve; while most airports need to invest heavily to compensate the losses from “aircraft handling” by doing their best to increase “non-aviation revenue”, while this is daily life today, airlines demand airports to invest into those technologies and development and process improvements, but are not willing to pay. Did Swiss pay a Penny (Rappen) for the improved deicing at their home airport? Make a guess.
And while the airlines benefit, I hear from the airports that they do not show any interest in A-CDM and A-CDM improvements. While they cut into the flesh on most airport’s fees, while they let them starve; while most airports need to invest heavily to compensate the losses from “aircraft handling” by doing their best to increase “non-aviation revenue”, while this is daily life today, airlines demand airports to invest into those technologies and development and process improvements, but are not willing to pay. Did Swiss pay a Penny (Rappen) for the improved deicing at their home airport? Make a guess.

 Mark from OAG directed my attention this week on OAG’s Punctuality League, which they offer for free
Mark from OAG directed my attention this week on OAG’s Punctuality League, which they offer for free  It can only be an indicator, as both sources fail to relate the one to the other. My first question would be to correlate the on-time performance to the hub airlines. Because it is utterly unfair to blame an airport, if their major hub airline is notoriously late.
It can only be an indicator, as both sources fail to relate the one to the other. My first question would be to correlate the on-time performance to the hub airlines. Because it is utterly unfair to blame an airport, if their major hub airline is notoriously late. Yes, for CheckIn.com we emphasize that all that data can only be indicators. To be interpreted by an experienced network planner. Because a single new flight makes a major impact on a new or small airport, but has little statistical relevance on a major hub. Saying that, isochrones are in itself valuable statistical data and we put them into our analyses for a reason. As they are a necessity in comparison with the catchment area analysis to interpret the possible impact for a route. In forecasting, you work with indicators, you have no facts.
Yes, for CheckIn.com we emphasize that all that data can only be indicators. To be interpreted by an experienced network planner. Because a single new flight makes a major impact on a new or small airport, but has little statistical relevance on a major hub. Saying that, isochrones are in itself valuable statistical data and we put them into our analyses for a reason. As they are a necessity in comparison with the catchment area analysis to interpret the possible impact for a route. In forecasting, you work with indicators, you have no facts. At the same time you work with big data, so the more data you work with, the more vital it is to get them from a sound source and have them integrated into a common system. Whereas most established data providers, be it OAG, Flight Stats, SITA, etc. have not yet addressed that for a “good reason”. But as an industry, it is vital we add this and integration is very high on our back log at CheckIn.com of what we where we want to go!
At the same time you work with big data, so the more data you work with, the more vital it is to get them from a sound source and have them integrated into a common system. Whereas most established data providers, be it OAG, Flight Stats, SITA, etc. have not yet addressed that for a “good reason”. But as an industry, it is vital we add this and integration is very high on our back log at CheckIn.com of what we where we want to go!




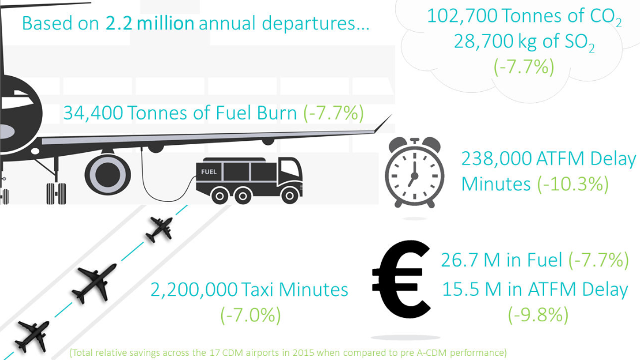


 With increasing legal demand to reimburse passengers on late or canceled flights beyond the value of their net fare they paid, this is were money for the airline is burned. And impact of disruptions and delays at the airport or in the air space may be a nuisance for the work at the airport or the air traffic controllers, but they have a commercial impact on the airline:
With increasing legal demand to reimburse passengers on late or canceled flights beyond the value of their net fare they paid, this is were money for the airline is burned. And impact of disruptions and delays at the airport or in the air space may be a nuisance for the work at the airport or the air traffic controllers, but they have a commercial impact on the airline: One discussion a few days ago addressed the definition of “departure”. And it is such a basic difference in definition, it hit me like a hammer, making me understand the impact of that different perception! When air traffic control talks about departure, they talk about the take-off of the aircraft (ATOT). When the airline and airports talk about the departure, they often talk about the time, the aircraft leaves it’s parking position at the terminal or on the apron, the off-block-time (AOBT). I had trouble, understanding, why an airport should invest into a “Pre-Departure Sequencer” instead of a DMAN in the delair-definition. The difference is based on the same subtle misperception of departure. The PDS and most “DMANs” out there focus on the TOBT, taking somewhat into account the delivery of the aircraft “in time” to the runway. Based on a rather “static” assumption of ATC capacity. The DMAN in delair perception optimizes the “real” departure. Taking into account minimum separation of aircraft, depending on the Standard Instrument Departure (SID) route and other highly complex parameters, the DMAN calculates the best TOBT. Thus, no matter the general disruptions at the airport and the real throughput on the runway by ATC, it delivers as many aircraft as possible for departure. That maximises the throughput and in turn minimizing the recovery time after general delays or disruptions.
One discussion a few days ago addressed the definition of “departure”. And it is such a basic difference in definition, it hit me like a hammer, making me understand the impact of that different perception! When air traffic control talks about departure, they talk about the take-off of the aircraft (ATOT). When the airline and airports talk about the departure, they often talk about the time, the aircraft leaves it’s parking position at the terminal or on the apron, the off-block-time (AOBT). I had trouble, understanding, why an airport should invest into a “Pre-Departure Sequencer” instead of a DMAN in the delair-definition. The difference is based on the same subtle misperception of departure. The PDS and most “DMANs” out there focus on the TOBT, taking somewhat into account the delivery of the aircraft “in time” to the runway. Based on a rather “static” assumption of ATC capacity. The DMAN in delair perception optimizes the “real” departure. Taking into account minimum separation of aircraft, depending on the Standard Instrument Departure (SID) route and other highly complex parameters, the DMAN calculates the best TOBT. Thus, no matter the general disruptions at the airport and the real throughput on the runway by ATC, it delivers as many aircraft as possible for departure. That maximises the throughput and in turn minimizing the recovery time after general delays or disruptions.