The Travel Industry and the Cloud
 Back in 2000, in my presentation at ITB Travel Technology Congress, I addressed the changes e-Commerce brought to our distribution. Aviation and travel have a very strong history in what we today experience as “new”, call “cloud computing”.
Back in 2000, in my presentation at ITB Travel Technology Congress, I addressed the changes e-Commerce brought to our distribution. Aviation and travel have a very strong history in what we today experience as “new”, call “cloud computing”.
Aviation has been a pacemaker in pre-Internet e-Commerce. Since the invention of the first “computerized reservation systems” (CRS), based on American’s ground-breaking development of the “Semi-Automated Business Research Environement” (Sabre). Read the Sabre-History for more. Thanks to the global SITA communications network (yes, those guys I temporarily worked for last year after they acquired my employer), aviation appreciated near instantaneous communication ever since I started working in aviation back in the late 80s. What we call e-Mail today, we called “Queue Messages” back then. To date, bookings, called “Passenger Name Records” (PNR) are created and maintained “in the cloud”. Whereas the “cloud based server” is either one of the Global Distribution Systems (GDS) and/or the airline’s own CRS.
Airline IT-managers celebrating this as the next big thing simply sell you old wine in new barrels. In the mid 90s, just about 20 years ago, the last “dummy terminals” were taken out of service, replaced by PCs with more sophisticated interfaces. Which were meanwhile very much replaced by web-clients working in standard browsers. The only difference being that those browsers often still use closed networks (such as SITA) for data transport instead of the Internet. Aside the obviously more reliable and stable data speed, this directly leads to the next question:
Cloud Security
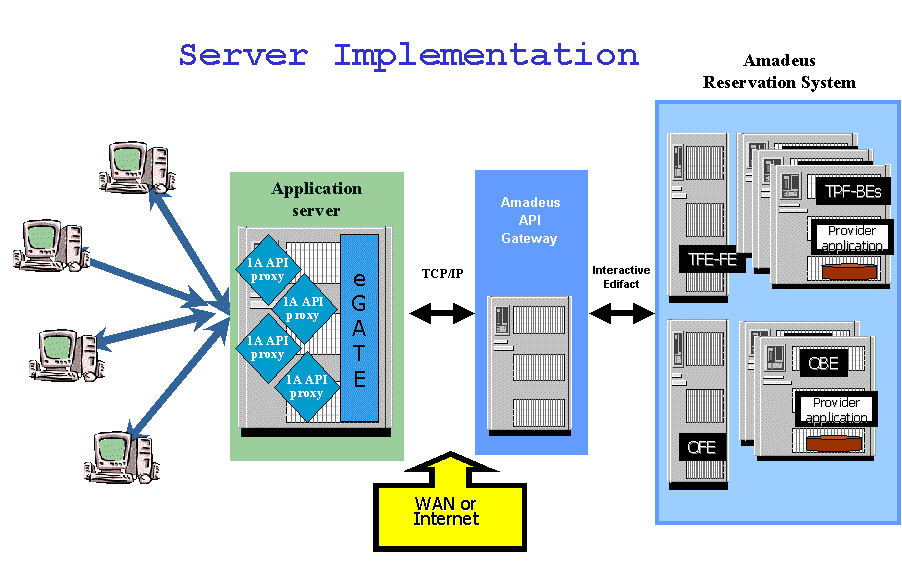 Where the GDS and CRS frequently work in a closed environment reducing the danger of hacking and other insecurities, recent developments make those services available through Internet links. Being a commodity, this is much cheaper. But it also opens the communication to a number of security issues. It needs complex security layers to avoid hacking or other unintended communication disrupting those large host systems. And this is also important to understand. “working in the cloud” is “clouding” (disguising) reality with fuzzy, hip wording. All it is is communicating through the cloud (word used to disguise “the Internet”) with servers that are not local but “elsewhere”.
Where the GDS and CRS frequently work in a closed environment reducing the danger of hacking and other insecurities, recent developments make those services available through Internet links. Being a commodity, this is much cheaper. But it also opens the communication to a number of security issues. It needs complex security layers to avoid hacking or other unintended communication disrupting those large host systems. And this is also important to understand. “working in the cloud” is “clouding” (disguising) reality with fuzzy, hip wording. All it is is communicating through the cloud (word used to disguise “the Internet”) with servers that are not local but “elsewhere”.

The cloud servers of Apple, Amazon, Microsoft, Amadeus, Worldspan or Sabre. Where the “Sabre” computers have been sold to HP and Sabre uses “commercial services”, Amadeus still has it’s own and also publishes quite some diagrams and images I frequently refer to.
But a fact in all such cases: If you believe it’s your data, this is a self-deception. You got to trust the company where you store your data to be trustworthy. Whereas recently there are quite some concerns about governmental insight into data. As I mentioned back in 2008, it’s questionable if a national government demands access to data without guarantee that this confidential commercial information does not reach the company’s competitor in that country. The example was not Russian, but American. Who watches the watcher?
 As I mentioned in my ITB presentation 2004, there’s possibilities to use alternate services from the Open Source developments. With cloud computing, you’re no longer required to use commercial services: I recently shifted all my personal data, especially calendar and contacts from Google into my OwnCloud. I trust my friend maintaining my own server. It’s in a huge computer center but my friend secures it against “unfriendly” or unauthorized access. And I hope what I have is not interesting to the server center operator to have someone physically accessing my server to steal data. A theoretical possibility. It’s a (semi-constant) assessment, on who to trust.
As I mentioned in my ITB presentation 2004, there’s possibilities to use alternate services from the Open Source developments. With cloud computing, you’re no longer required to use commercial services: I recently shifted all my personal data, especially calendar and contacts from Google into my OwnCloud. I trust my friend maintaining my own server. It’s in a huge computer center but my friend secures it against “unfriendly” or unauthorized access. And I hope what I have is not interesting to the server center operator to have someone physically accessing my server to steal data. A theoretical possibility. It’s a (semi-constant) assessment, on who to trust.
I also mentioned in my 2013 blog about Big Data, “The first, Big-Data-experts came up with, have been personal profiles, coming from a variety of different sources. That Google and Facebook still offer me young Russian ladies for marriage is a good sign that they are way off even that goal.” It’s a simple question on big data. From the same post: “And as the amount of data grows faster than the processing power, the real problem is predictable.”
Open Data
As much as you want to keep your personal and commercial data in some areas private, there was a mantra in the 90s “My data is my capital”. It was the time the Internet started to make data available to everyone and who “owned” the data could sell it expensively. To date the value of the GDS, the OAGs, Albatross, CH Aviation and other such data collecting companies. Whereas it is relatively easy to process aviation data as most of it is very clearly standardized. But as much as the data processing adds some value, it’s life cycle is ending. More and more “common data” becomes available openly. Where that i.e. started with OpenStreetMap, meanwhile the basic cadaster (land registry) data like street data, administrative boundaries, etc. are made openly available. Others still try to charge horrendous amounts, but they become a minority and will become extinct soon. The value is no longer in “owning” the data, but in meaningful analysis and use of it.
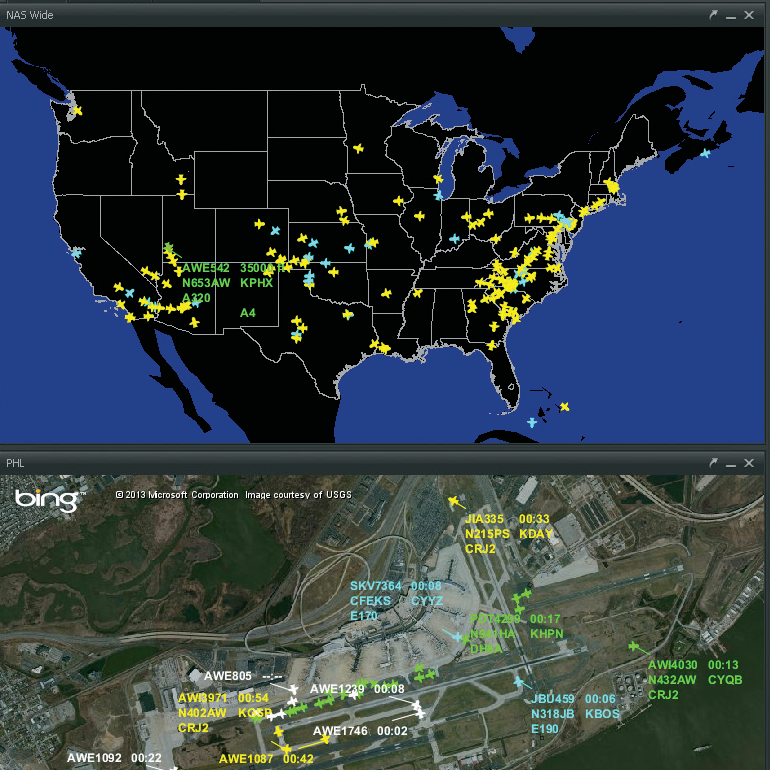 Having been pacemakers in e-Commerce, aviation today is light years behind other industries. U.S. tools showing aircraft in-flight on maps like Harris Corp. (Exelis) NextVue does not have access to Canadian data as NAV Canada wants to sell it. Expensively. Not exchange (to also have access to U.S. data). It’s mine. Such, planes not traveling to/from the U.S. airspace simply don’t show. And the NAV Canada data is very often “a problem” for webservices providing such information in other markets. Dear NAV Canada, this is your wake-up call. The same for many other government owned “businesses”. Open Data is here. If you don’t come along, you will find yourself bypassed before long.
Having been pacemakers in e-Commerce, aviation today is light years behind other industries. U.S. tools showing aircraft in-flight on maps like Harris Corp. (Exelis) NextVue does not have access to Canadian data as NAV Canada wants to sell it. Expensively. Not exchange (to also have access to U.S. data). It’s mine. Such, planes not traveling to/from the U.S. airspace simply don’t show. And the NAV Canada data is very often “a problem” for webservices providing such information in other markets. Dear NAV Canada, this is your wake-up call. The same for many other government owned “businesses”. Open Data is here. If you don’t come along, you will find yourself bypassed before long.
The same experience I had in my past years working on Airport Collaborative Decision Making (A-CDM). As long as our industry does not learn that it is in the benefit to the entire business and industry to share work data at reasonable cost. Base data is freely available today. But it’s fascinating how much of the base data we get from the “official sources” (like IATA, ICAO and the likes) is of lousy quality requiring manual review and updates.
That’s aviation. Believe me, working with data from 33 countries in Europe so far, basic data like population on municipality level, associating that to commercial or openly available map data from the same country’s cadastre … It’s a challenge. Many countries where the name of a city is not unique, but a municipality may have three four different names in the country. Not to mention that there are duplicate municipality names even within the same state. Open data is needed, but I think it might be something if a country could decide on unique naming for a given municipality and if EuroStat and the national statistics offices could agree on a unique identifier. And make sure their data matches. Else, a lot of people in the world will have a full time job to repeat the stunt we did. And other such data correcting others did. Again. And again. And again again.
The Internet of Things
 The last weeks the messages on LinkedIn, hyping the “Internet of Things” (IoT) are “exploding”. At this point, it’s very much like “Big Data”. Because just like big data, the concerns mentioned above apply. As long as everyone does something different and there is no common understanding about how to connect the IoT, it’s a lot of smoke and distracting noise, but not too much on real results. No matter if it’s global players announcing their understanding of IoT. As long as they don’t agree and establish open standards, IoT is a buzz word with not much substance.
The last weeks the messages on LinkedIn, hyping the “Internet of Things” (IoT) are “exploding”. At this point, it’s very much like “Big Data”. Because just like big data, the concerns mentioned above apply. As long as everyone does something different and there is no common understanding about how to connect the IoT, it’s a lot of smoke and distracting noise, but not too much on real results. No matter if it’s global players announcing their understanding of IoT. As long as they don’t agree and establish open standards, IoT is a buzz word with not much substance.
As an example from another industry, more common to us all: For many years I have a look at “house IoT”. It would be so nice to be able to have the thermostats and blinds being programmable. Unfortunately, all makers of “intelligent” thermostats have their own “standard”, making it impossible to mix them. So if you want to buy, you got to select the system. And you’re stuck with it… That’s like the times of VHS vs. Betamax or DVD±R, where you usually selected the wrong technology…
Just as “video tape” or “DVD” came, evolved a standard and then became household normality, the IoT will need to develop common standards to allow common tools to exchange information with them in a default way. And not have 150 different “interpreters” trying to talk to all those devices in their language…
Food for Thought
Comments welcome!
![“Our Heads Are Round so our Thoughts Can Change Direction” [Francis Picabia]](https://foodforthought.barthel.eu/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/Picabia-Francis-Round-Heads.jpg)
Comments
Interesting thoughts on big data and the internet of things. Would be nice to have shutters, intelligent thermostats, pool filters, house lights, etc that communicate in the same language. Hopefully the most efficient and capable system will evolve. In the meantime, I will hold off on diving in to the technology, until I know who Betamax and VHS are….
Cheers